G.V() is now compatible with Oracle Graph
Introduction
As revealed in our latest update, we’re delighted to announce that G.V() is now fully compatible with Oracle Graph in Oracle Database. We’ve been collaborating directly with the Oracle team to make this possible and we’re excited to welcome Oracle Graph users into our community.
Oracle has long been known for their pioneering database management system and their role in developing the modern SQL standard. Oracle Graph is a feature of Oracle Database. It offers all the benefits of graph pattern matching and analytics, while leveraging the relational engine for set-oriented operations in a graph query, without the hurdles of deploying and maintaining a separate graph database. Oracle Database 23ai is the first commercial database vendor to implement the SQL:2023 query language, which allows users to perform graph analysis with SQL.
Oracle Graph is a perfect partner to G.V(), which is why we were eager to make our product available to Oracle customers. Connecting your Oracle Database to G.V() takes only seconds. Once connected, you can explore your data using either G.V()’s own intuitive interface or our integrated support for the SQL:2023 query language. You can try this for yourself using Oracle Database 23ai Free if you’re not already running Oracle Databases.
Let’s dive into what G.V() can do with Oracle Database.
Get connected instantly
Connect to Oracle Database 23ai in just 1, 2, 3!
All you need is your JDBC connection string and log-in credentials. There’s no limit to how many connections you can make like this – you can easily connect to multiple graphs within your database at the same time, or even graphs within multiple Oracle databases – all concurrently.

Turn SQL:2023 queries to graph visualizations instantly
G.V() turns your graph queries into an interactive, large-scale graph visualization effortlessly, creating a whole new way to navigate your relational data on Oracle Graph.
Our high-performance graph rendering engine offers the perfect balance between customization and speed by leveraging GPU-based computing, compatible with any device or specification.
You don’t need to do anything – just write and run your query. G.V() will handle the visualization instantly:
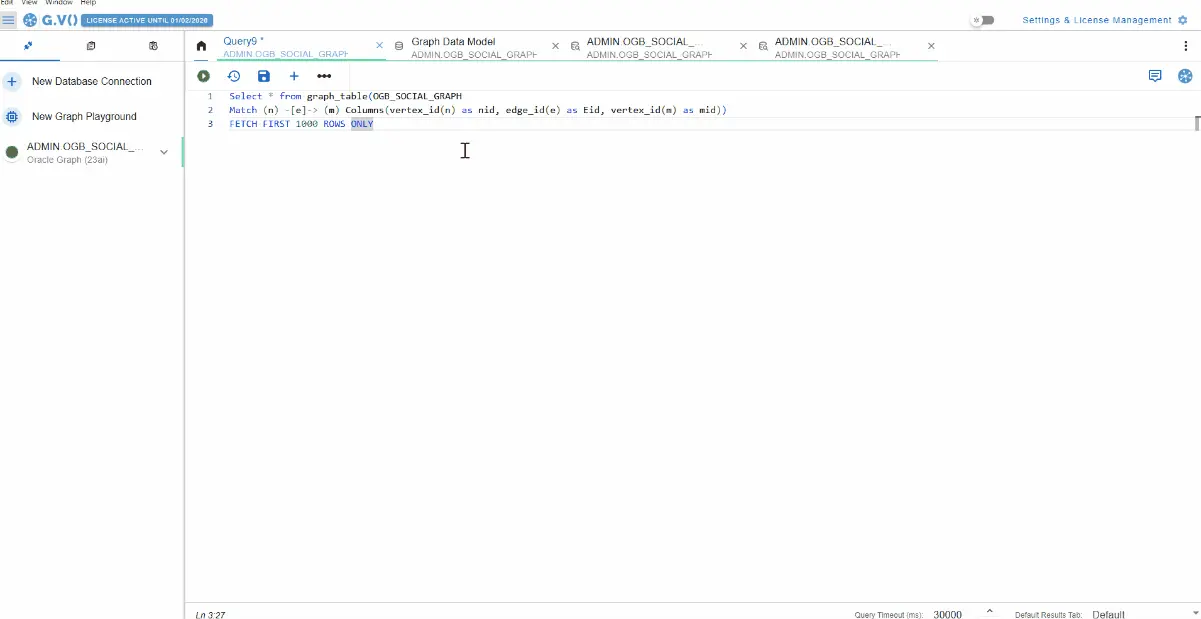
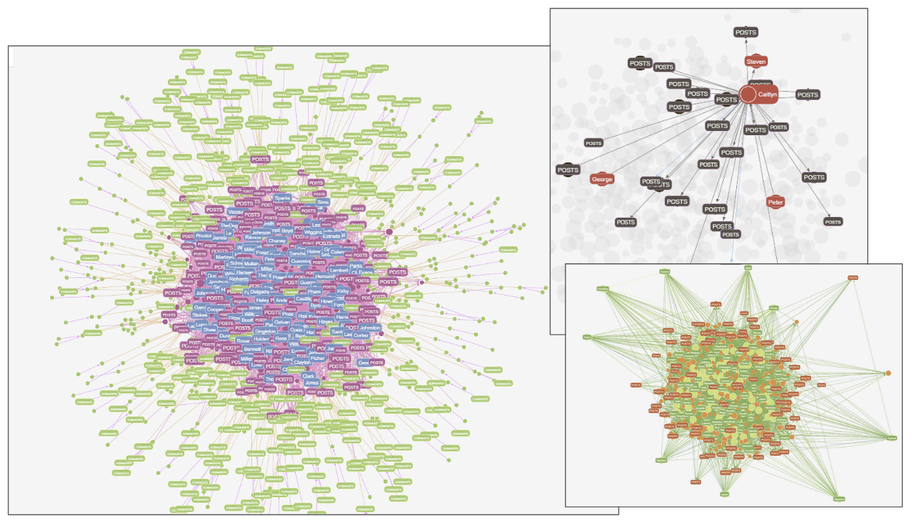
Visualize graph databases instantly in G.V().
But that’s not all – here are just a few examples of ways you can visualize your Oracle Graph data using G.V():
- All kinds of layout configurations, data filters and aesthetic options to make the most of your visualization
- Interactive data exploration to load and filter additional elements into the graph
- Table view for when you just need to see your data in a structured, organized format
- JSON data outputs that are versatile and developer friendly to export your data anywhere
- Object browser to navigate complex and hierarchical data
Explore data intuitively
At G.V(), we want to make data exploration as easy as possible. Our intuitive interface lets you navigate your database without needing to write a single query. Every part of your data can be accessed interactively from the GUI, no code required!
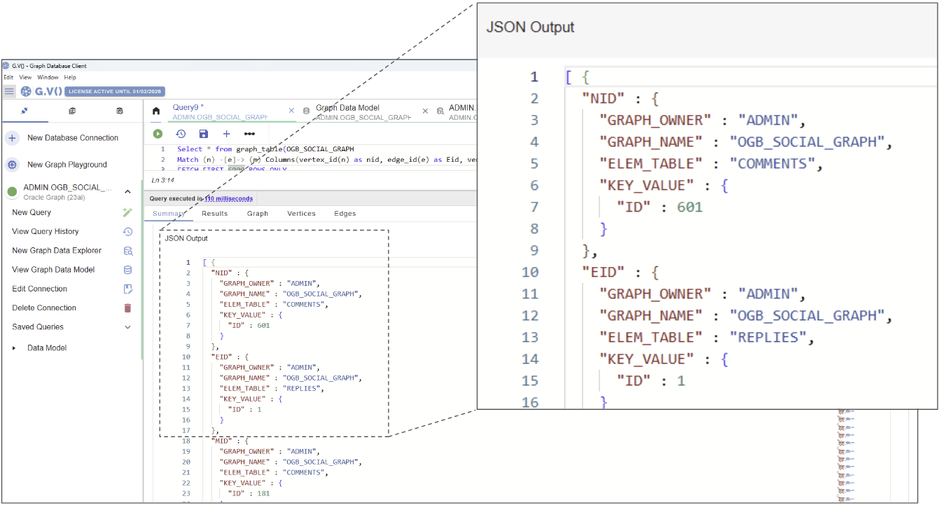
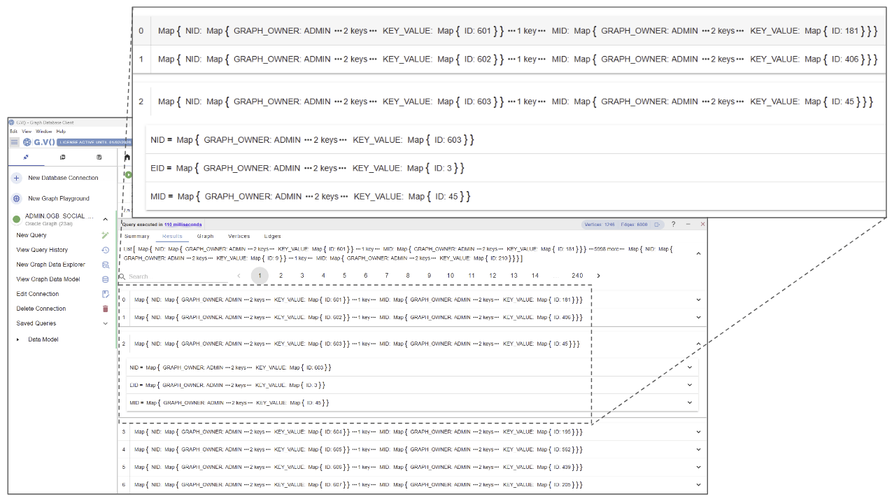
Our Graph Data Explorer makes no-code exploration available with just a few clicks. You can build complex path patterns using labels and property filters to create advanced queries in plain text language.
Let’s use Oracle’s freely available social media database as an example. See how easy it is to search for all the posts created by the user laurajohnson@oracleemail.com and the users who have commented on those posts:
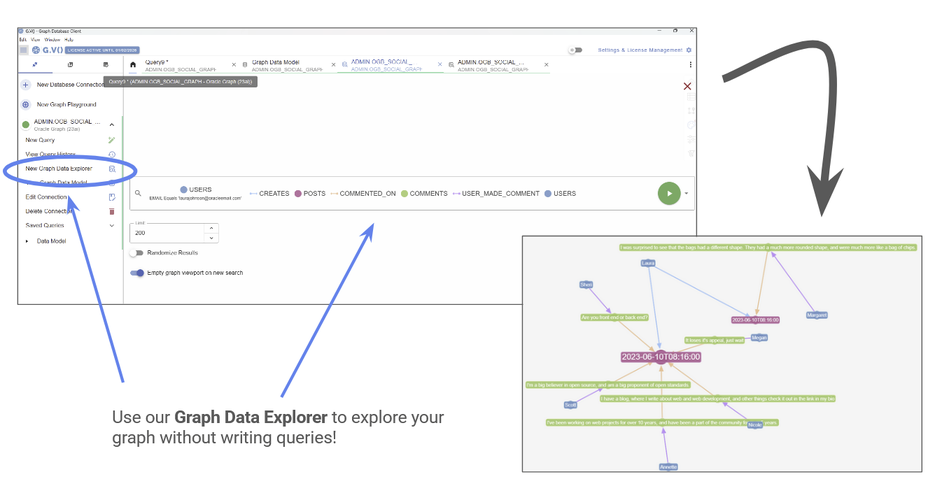
Use the Graph Data Explorer to explore your database without entering queries.
Visualize your graph data schema with ease
It can be challenging to keep track of your data structures, particularly if your model keeps evolving to accommodate new use cases and applications. Fortunately, G.V() lets you keep track of your Graph Data Model as it evolves in real time.
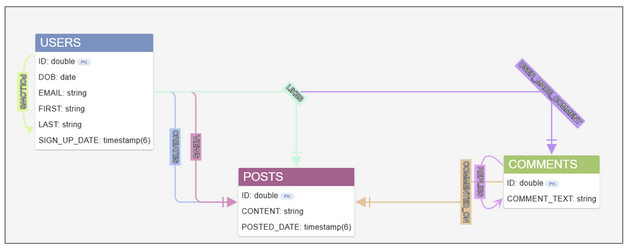
View the data model of your database within G.V().
The data model view screen lets you visualize your data relationships as an abstract model. This gives you a bird’s eye view, letting you get an overall picture of how nodes and edges are connected at a quick glance.
Conclusion
We’re so excited to welcome the existing Oracle community to G.V(), and invite you to try using the G.V() + Oracle Database 23ai combination. It’s a great pairing that gives you all the advantages of both relational and graph databases.
Keep an eye out for further updates on our integration with Oracle. It’s been a pleasure working with the team, and we expect this is only the start of our collaboration!